The academic rank of Bachelor is a full-fledged degree. It offers the quickest route to obtaining a university degree. It is also a stepping stone to studying for a Master’s degree; however, it also opens the way for entering directly on a career path.
Bachelor of Arts (B.A.) and Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) degrees
Degrees are awarded to signify a successful completion of academic studies. There are two types of Bachelor’s degrees at the University of Stuttgart. They rank equally but differ by field of specialization:
- Bachelor of Arts (B.A.) is awarded in the humanities and social science fields. Also, when studying for a teaching qualification a Bachelor of Arts degree must be earned first.
- Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) is awarded in the natural sciences, engineering sciences, and economics fields.
Teaching qualification
All information on studying for a teaching degree is published on our teaching degree website.
The basics of Bachelor’s degree studies
Normally, study programs leading to the Bachelor of Arts (B.A.) and Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) degrees take six semesters to complete. Latest in your third year of studies it is possible to choose an individualized direction for your program of studies, that is, a given specialization within the subject area.
In addition to the standard period of study, which is 6 semesters, there is also the maximum length of study. It is usually 10 semesters and is laid down in the exam regulations. This means that you generally have up to ten semesters to complete your bachelor’s degree.
Your study program is composed of various modules. A module, in turn, consists of one or more courses, which are linked in terms of content and are rounded off thematically. A module is completed by passing an exam, by handing in a written assignment or term paper, or by another verifiable achievement.
The Bachelor's programs consists of:
- Subject modules (basic, core, and additional modules)
- Key qualification modules (both subject-specific skills and skills that lie outside the subject field)
- a Bachelor's thesis (an independent scientific treatment)
For a completed module you will receive ECTS credits. A single ECTS credit approximates a 30-hour work load per semester.
The number of credits for a module reflects the approximate time required for a given course. From the expected number of credits, you can calculate how much of your time a module will take up.
In a Bachelor's program a total of 180 ECTS credits must be earned (30 ECTS credits per semester). More detailed information on these terms is published in our glossary, the University A-Z.
You can use the curriculum (in German: Studienverlaufsplan) to find out
- what course contents a study program has,
- which weighting is given to the individual modules, and
- how the study program is structured.
The curriculum is therefore very suitable for comparing study programs.
Curricula are available as PDF files, and as interactive curricula integrated in the Higher Education Compass for choosing a study program. The symbols used in the interactive curriculum are also used in the module descriptions below.
There are three types of modules. Depending on the study program, other designations may also be used.
| Symbol in the interactive curriculum | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Basic modules: convey basic methodical and methodological knowledge |
 |
Core modules: convey the actual subject-specific knowledge |
 |
Additional modules: here you have a certain freedom of choice, usually from the fifth semester. In some curricula, additional modules are also called electives. |
 |
Key competencies (SQ) are designed to equip students for a professional career. They do not convey pure subject knowledge, but instead focus on teaching capabilities and competencies. This is why some SQ courses are interdisciplinary.
| Symbol in the interactive curriculum | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Key competencies: here you acquire both subject-related ("subject-affine") and interdisciplinary skills |
You focus on one subject. This is the common model in the natural sciences, engineering, and mathematics. There are also single-subject Bachelor’s degree programs available in other disciplines.
In the natural and engineering sciences and in mathematics, you will receive a Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) degree. In the study programs of the cultural and social sciences, you will receive a Bachelor of Arts (B.A.) degree.
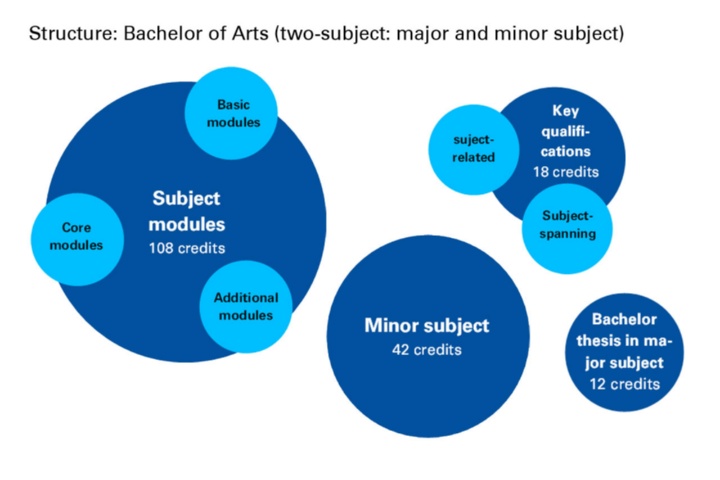
In the combined Bachelor’s degree program, you study a major and a minor. Combined Bachelor’s degrees (or two-subject Bachelor’s degrees) are available especially in the cultural and social sciences. A special feature of the University of Stuttgart is that you can also choose a minor from a selection of science and engineering disciplines.
The modules of the major subject comprise 108 ECTS credits, the modules of the minor comprise 42. In addition, there is the Bachelor's thesis in the major subject with 12 credits and key competencies with 18 credits.
The Bachelor’s thesis is written in the major subject. The postgraduate Master’s degree program is generally based on the major subject that was chosen in the two-subject Bachelor’s degree program.
Subject combinations in the Bachelor of Arts - major and minor subjects
Options
In a combination Bachelor’s study program, each of these subjects must be combined with a different minor subject. For example, English selected as major may not be combined with English as a minor but could be combined with a minor in computer science.
Application deadline for combined bachelor’s degree programs:
Please be sure to check whether one of your chosen subjects has limited entry (with numerus clausus). If that is the case: the application deadline is 15 July.
In the following PDF file (not digitally accessible), the combinations of the above mentioned major and minor subjects are illustrated graphically.
Major subjects
- English
- Vocational Education / Technical Education
- German Literature
- History
- History of Natural Sciences and Technology
- Art History
- Linguistics
- Romance Studies
Minor subjects
- English
- Civil Engineering
- Vocational Education / Technical Education
- Business Administration
- Chemistry
- Computational Linguistics
- Electrical Engineering and Information Technology
- German Literature
- History
- History of Sciences and Technology
- Computer Science
- Art History
- Linguistics
- Mechanical Engineering
- Mathematics
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Romance Studies
- Sociology
- Sports Science
- Economics
Contact